OpenWrt Luaスクリプト専用UCI関数の使い方

今回は、OpenWrtのLuaスクリプト用UCI操作関数の使い方について紹介します。
このUCI操作関数は、WebUIのLuCIまたはLuCIと連携するCGIシステムがUCIコンフィグレーションファイルを操作するために使用しているものです。 luci.model.uciモジュールに収録されています。
これら関数の使い方を理解することで、UCIコンフィグレーションファイルを操作するCGIシステムの開発が容易になります。
関数仕様の詳細については既に公式ドキュメントに記載されています。 そのため、この記事ではサンプルコードとその実行結果を掲載することで使い方を説明します。
目次
- 実施環境
- サンプルコード用UCIコンフィグレーションファイル(/etc/config/sample)
- Luaスクリプト用UCI操作関数を使用する上で重要な知識
- モジュールロード
- Luaスクリプト用UCI操作関数の使い方
- Cursor:add
- Cursor:apply
- Cursor:changes
- Cursor:commit
- Cursor:confirm
- Cursor:delete
- Cursor:delete_all
- Cursor:foreach
- Cursor:get
- Cursor:get_all
- Cursor:get_bool
- Cursor:get_confdir
- Cursor:get_first
- Cursor:get_list
- Cursor:get_savedir
- Cursor:get_session_id
- Cursor:load
- Cursor:revert
- Cursor:rollback
- Cursor:rollback_pending
- Cursor:save
- Cursor:section
- Cursor:set
- Cursor:set_confdir
- Cursor:set_list
- Cursor:set_savedir
- Cursor:set_session_id
- Cursor:substate
- Cursor:tset
- Cursor:unload
- Cursor:reorder
実施環境
この記事は以下の環境で実施した結果を元に作成しています。
- #OpenWrtデバイス
- 名称:Raspberry Pi3 Model B
- CPU:ARM Cortex-A53 (1.2GHz)
- SOC:Broadcom BCM2837
- RAM:1GB
- ストレージ(media):MicroSDカード
- #OpenWrt
- OpenWrt 22.03
- #Lua
- Ver 5.1.5
- #依存パッケージ
- luci-compat
※opkg install luci-compatまたは、bulidrootのmake menuconfigによるluci-compat指定により導入してください。 - lua5.3(今回はver5.3を使用しましたが最新版であればOKなはずです。)
※opkg install luaまたは、buildrootのmake menuconfigによるlua指定により導入してください。
サンプルコード用UCIコンフィグレーションファイル(/etc/config/sample)
掲載サンプルコードの操作対象ファイルは、この記事のために作成したUCIコンフィグレーションファイル(/etc/config/sample)です。
このUCIコンフィグレーションファイルはUCIコマンドを使用して作成できます。 読者ご自身の環境で、サンプルコードを実行したい場合は、お手持ちのOpenWrtデバイスのコンソール上で以下のUCIコマンドを実行してください。
root@OpenWrt:~# touch /etc/config/sample root@OpenWrt:~# uci batch << EOI > set sample.sectionA=type > set sample.sectionA.flag1=on > set sample.sectionA.flag2=off > set sample.sectionA.flag3=true > set sample.sectionA.flag4=false > set sample.sectionA.flag5=1 > set sample.sectionA.flag6=0 > set sample.sectionB=type > set sample.sectionB.value=100 > set sample.sectionC=type > add_list sample.sectionC.items=1 > add_list sample.sectionC.items=2 > add_list sample.sectionC.items=3 > add_list sample.sectionC.items=4 > add_list sample.sectionC.items=5 > add sample unname > set sample.@unname[0].value=100 > add sample unname > set sample.@unname[1].value=200 > add sample unname > set sample.@unname[2].value=300 > EOI root@OpenWrt:~# uci commit sample
上記のコマンド実行後、catコマンドでsampleファイルの中身を見てみると、次のように表示されるはずです。
root@OpenWrt:~# cat /etc/config/sample
config confirm 'sectionA'
option flag1 'on'
option flag2 'off'
option flag3 'true'
option flag4 'false'
option flag5 '1'
option flag6 '0'
config confirm 'sectionB'
option value '100'
config confirm 'sectionC'
list items '1'
list items '2'
list items '3'
list items '4'
list items '5'
config uname
option value '100'
config uname
option value '200'
config uname
option value '300'
以上より、この記事では、/etc/config/sampleに対してUCI操作をするコードを掲載します。 これを通してLuaスクリプト用UCI操作関数について、その使い方を理解して頂ければ幸いです。 それでは、次節から説明に入ります。
Luaスクリプト用UCI操作関数を使用する上で重要な知識
Luaスクリプト用UCI操作関数を使用する上で重要なことの1つにステージング領域の選択があります。
Luaスクリプト用UCI操作関数は元々、LuCIで利用されることを目的に実装されています。そのため、ユーザーの通信セッションに 紐づくメモリ領域をステージング領域として使用するか否かでその後の設定データの保存先が変わる特徴を持っています。
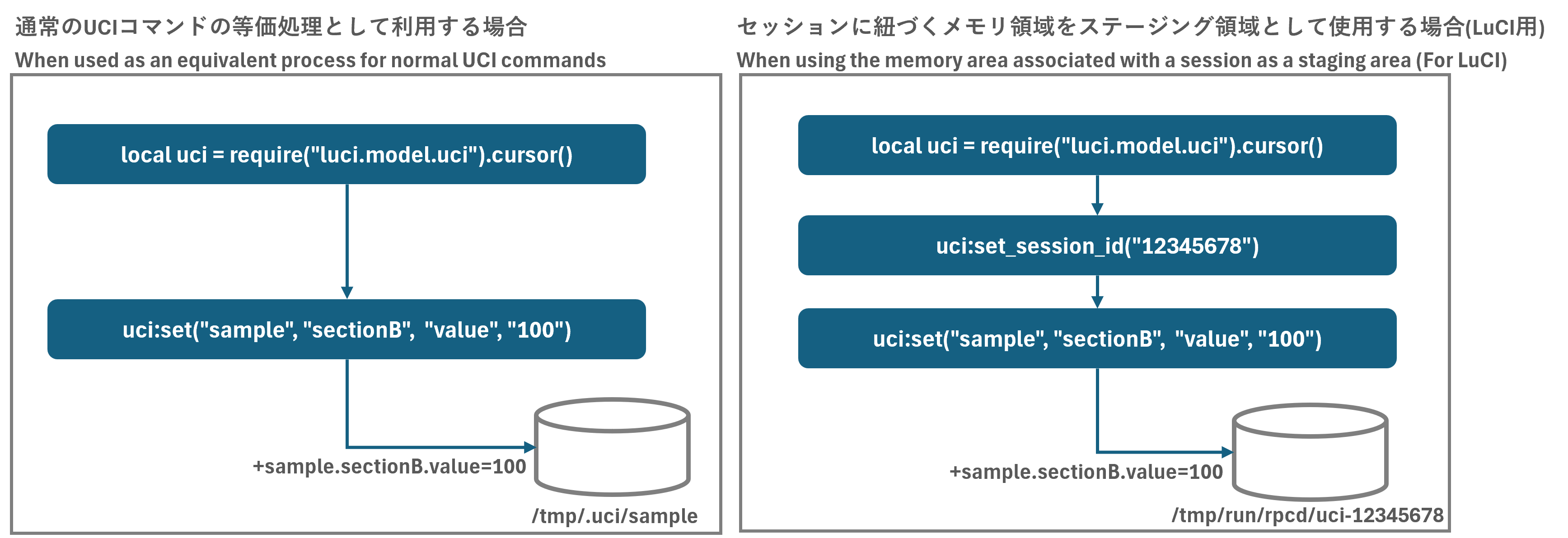
もし、実装者の方がステージング領域を/tmp/.uciとする通常のUCIコマンド(/usr/bin/uci)の完全等価処理として これらのUCI操作関数を使用したい場合、必須モジュールのluci.model.uciをインポートした後にそのままset関数など 呼び出せば設定変更は/tmp/.uciに保存されます。
逆に通信セッションに紐づくメモリ領域/tmp/run/rpcd/uci-<ubus_rpc_session>を指定したい場合、 必須モジュールluci.model.uciをインポートした後にset_session_id関数を実行してメモリ領域(/tmp/run/rpcd/-<ubus_rpc_session>)作成する必要があります。
set_session_id関数によってメモリ領域を確保した後は、set関数などのUCI操作関数による設定変更は全てそのメモリ領域にコピーされます。
このように、Luaスクリプト用UCI操作関数にはステージング領域の決定方法に特徴がありますので、そのことは理解していた方が良いと思います。 次節ではこのことを踏まえて説明します。
モジュールロード
今回のLuaスクリプト用UCI操作関数を使用するためには、事前準備として luci.model.uciモジュールをロードし、その中から関数の情報が格納されたテーブルを取得する必要があります。 モジュールをロードして、テーブルを取得するには以下の2つの方法があります。
- cursor()
- 通常、Luaスクリプト上でUCI操作関数を使用する際は、本関数を次のように呼び出します。
-
local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() - これにより、以降はuci変数を通して、各UCI操作関数を実行することが可能になります。
- そのため、この記事の掲載サンプルコードは、各UCI操作関数を本関数によって取得されたをLuaテーブルを経由して実行します。
- cursor_state()
- 現在(2024/10/14)の実装では、curor()と同じ定義内容になっているため、エイリアスとして機能しています。 今後、実装が追加されるかもしれません。
-
local uci = require("luci").cursor_state()
Luaスクリプト用UCI操作関数の使い方
各UCI操作関数についてサンプルコードとその実行結果を掲載し、説明します。
- Cursor:add(config, type)
-
LuCI連携なし
add関数は任意のUCIコンフィグレーションファイルに対して匿名セクションを作成します。 作成された匿名セクションはステージング領域(default: /tmp/.uci)に保存されます。 静的データとして確定したい場合は、commit関数によってフラッシュ領域(default: /etc/config)にコピー(マージ)する必要があります。 -
次はsampleコンフィグ配下にtestタイプの匿名セクションを作成するサンプルコードです。
-- add_test1.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() uci:add("sample", "test") -
実行してみると、ステージング領域のsampleファイルにtestタイプの匿名セクションが作成されることが確認できます。
root@OpenWrt:~# lua add_test.lua root@OpenWrt:~# cat /tmp/.uci/sample --catの代わりにuci changesでも同様の結果が表示されます。 +sample.cfg046865='test' -
LuCI連携あり
set_session_idでセッション番号をuciオブジェクトに割り当てた場合、uci:addによって追加された匿名セクションなどの ステージング領域は/tmp/.uciではなく、セッション番号に紐づけられたメモリ領域になります。 - 次はセッション番号指定によって、それに対応するメモリ領域を確保した上でsampleコンフィグ配下にtestタイプの匿名セクションを作成するサンプルコードです。
-
-- add_test1.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() local result = uci:set_session_id("0479472194661836394729210") if result then local id = uci:get_session_id() print("success : id =" .. id) else print("failed") return end uci:add("sample", "test") - 動作確認はubus monitorコマンドを実行した後に本サンプルコードを実行します。
-
root@OpenWrt:~# ubus monitor & root@OpenWrt:~# lua add_test2.lua
- 実行してみると以下のようにセッション番号と対応するメモリ領域(/tmp/run/uci-<ubus_rpc_session>)に変更内容が記録されたことがわかります。 メモリ領域を管理しているのは/sbin/rpcdです。
- ----->Cursor:add関数仕様
- Cursor:apply(rollback) ※作成中です。
-
-- add_apply.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() - ----->Cursor:apply関数仕様
- Cursor:changes(config)
- changes関数はステージング領域(default: /tmp/.uci)に保存された変更内容をLuaテーブルとして取得する関数です。
-
次は、sample.sectionB.valueの値を初期値の"100"から"hello"に変更し、ステージング領域に
保存した変更内容をコンソールに表示するサンプルコードです。
-- changes_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() -- uci:set関数で以下のsampleコンフィグ設定を変更 -- 新規データとして、sample.sectionB.value='hello'をステージング領域に保存します。 uci:set("sample", "sectionB", "value", "hello") local config_data = uci:changes("sample") -- ステージング領域のsampleコンフィグを表示 for _, table in ipairs(config_data) do for _, val in ipairs(table) do io.write(val .. " ") end io.write("\n") end
-
実行してみると、次のようにsampleコンフィグのステージング領域の変更内容が表示されます。
今回の場合では、sample.sectionB.valueが'hello'という値に更新(set)されたことがLuaテーブルの内容から分かります。
root@OpenWrt:~# lua changes_test.lua set sectionB value hello
- ----->Cursor:changes関数仕様
- Cursor:commit(config)
-
ステージング領域(default: /tmp/.uci)に保存された変更差分をフラッシュ領域(default: /etc/config)にコピー(マージ)します。
次はsample.sectionB.valueの値を初期値の"100"から"hello"に変更し、その変更内容をフラッシュ領域にコピー(マージ)するサンプルコードです。
-- commit_test.lua local loca uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() uci:set("sample", "sectionB", "value", "hello") uci:commit("sample") -
実行してみると、フラッシュ領域である/etc/config内の対応するUCIコンフィグレーションファイル(今回はsample)
に変更内容が反映されていることが確認できます。
root@OpenWrt:~# lua commit_test.lua root@OpenWrt:~# cat /etc/config/sample config type 'sectionA' option flag1 'on' option flag2 'off' option flag3 'true' option flag4 'false' option flag5 '1' option flag6 '0' config type 'sectionB' option value 'hello' config type 'sectionC' list items '1' list items '2' list items '3' list items '4' list items '5' - ----->Cursor:commit関数仕様
- Cursor:confirm() ※作成中です。
-
-- confirm_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() - ----->Cursor:confirm関数仕様
- Cursor:delete(config, section, option)
-
[1]:指定セクションを削除する
任意セクションを削除します。削除内容はステージング領域(default:/tmp/.uci)の対応するUCIコンフィグレーションファイルに 保存されます。次はsample.sectionBを削除するサンプルコードです。 -
-- delete_section_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() uci:delete("sample", "sectionB") -
実行してみると、ステージング領域に削除内容が保存されていることが確認できます。
通常、この後にcommit関数によってフラッシュ領域に削除内容をコピー(マージ)することで
sample.sectionBの削除が確定します。
root@OpenWrt:~# lua delete_section_test.lua root@OpenWrt:~# uci changes -sample.sectionB
-
[2]:指定オプションを削除する
任意セクションのオプションを削除します。削除内容はステージング領域(default:/tmp/.uci)の対応するUCIコンフィグレーションファイルに 保存されます。次はsample.sectionB.valueを削除するサンプルコードです。 -
-- delete_option_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() uci:delete("sample", "sectionB", "value") -
実行してみると、ステージング領域に削除内容が保存されていることが確認できます。
通常、この後にcommit関数によってフラッシュ領域に削除内容をコピー(マージ)することで
sample.sectionB.valueの削除が確定します。
root@OpenWrt:~# lua delete_option_test.lua root@OpenWrt:~# uci changes -sample.sectionB.value
- ----->Cursor:delete関数仕様
- Cursor:delete_all(config, type, comparator)
- 任意UCIコンフィグレーションファイル(config)の指定タイプ情報(type)を持つセクションを削除し、その変更内容をステージング領域(default: /tmp/.uci)に保存します。 このとき、第三引数にコールバック関数(comparator)を指定することで、削除対象セクションを本当に削除するか判定処理に掛けることができます。
- 次は、sampleコンフィグの"type"タイプを持つセクションで、名前が「sectionB」と「sectionA」のデータを削除するサンプルコードです。 コールバック関数としてcomparatorを定義し、その中でsectionBとsectionCの名前を持ったセクションを削除対象として最終決定しています。
-
-- delete_all_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() local call_cnt = 0 function output_msg(data, message) if type(data) == "table" then for key, val in pairs(data) do local _message = message .. "[" .. key .. "]" output_msg(val, _message) end elseif type(data) == "boolean" then if data == true then io.write(message .. " = true\n") elseif data == false then io.write(message .. " = false\n") end elseif type(data) == "string" or type(data) == "number" then io.write(message .. " = " .. data .. "\n") end end function comparator(table) local delete_flg = false call_cnt = call_cnt + 1 print("---------[CALLED FUNC No." .. call_cnt .. "]----------") for key, val in pairs(table) do local message = "table[" .. key .. "]" output_msg(val, message) io.flush() end -- sampleからセクション名「sectionB」、「sectionC」のデータを削除します if table[".name"] == "sectionB" then delete_flg = true elseif table[".name"] == "sectionC" then delete_flg = true end -- 返却値がtrueならセクションを削除します return delete_flg end uci:delete_all("sample", "type", comparator)
-
実行してみると、「sectionB」と「sectionC」という名のセクションが削除され、ステージング領域にその変更が保存されます。
root@OpenWrt:~# lua delete_all_test.lua ---------[CALLED FUNC No.1]---------- table[.name] = sectionB table[.type] = type table[value] = hello table[.anonymous] = false table[.index] = 1 ---------[CALLED FUNC No.2]---------- table[flag2] = off table[.anonymous] = false table[flag3] = true table[.index] = 0 table[flag4] = false table[flag6] = 0 table[flag5] = 1 table[flag1] = on table[.name] = sectionA table[.type] = type ---------[CALLED FUNC No.3]---------- table[.name] = sectionC table[.type] = type table[items][1] = 1 table[items][2] = 2 table[items][3] = 3 table[items][4] = 4 table[items][5] = 5 table[.anonymous] = false table[.index] = 2 root@OpenWrt:~# uci changes -sample.sectionB -sample.sectionC
- 上記結果から、コールバック関数は各セクションの読み込みごとに呼び出されることが分かります。 そして、コールバック関数の戻り値がtrueであれば、そのセクションは最終的な削除対象となります。
- ----->Cursor:delete_all関数仕様
- Cursor:foreach(config, type, callback)
- 任意UCIコンフィグレーションファイル(config)の指定タイプ情報(type)を持つセクションに対して、何等かの処理(callback)を実行したい場合に使用する イテレータ関数です。
- 次は、sampleコンフィグのconfirmタイプのセクションの中身を表示するサンプルコードです。 セクションの内容をコンソールに表示するコールバック関数を第三引数に指定することで、各対象セクションの読み込みごとに呼び出されます。
-
-- foreach_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() local call_cnt = 0 function output_msg(data, message) if type(data) == "table" then for key, val in pairs(data) do local _message = message .. "[" .. key .. "]" output_msg(val, _message) end elseif type(data) == "boolean" then if data == true then io.write(message .. " = true\n") elseif data == false then io.write(message .. " = false\n") end elseif type(data) == "string" or type(data) == "number" then io.write(message .. " = " .. data .. "\n") end end function callback(table) call_cnt = call_cnt + 1 print("---------[CALLED FUNC No." .. call_cnt .. "]----------") for key, val in pairs(table) do local message = "table[" .. key .. "]" output_msg(val, message) io.flush() end end uci:foreach("sample", "type", callback) -
実行してみると、各対象セクションごとにコールバック関数が呼び出され、展開されたLuaテーブルの内容が表示されます。
root@OpenWrt:~# lua foreach_test.lua ---------[CALLED FUNC No.1]---------- table[flag2] = off table[.anonymous] = false table[flag3] = true table[.index] = 0 table[flag4] = false table[flag6] = 0 table[flag5] = 1 table[flag1] = on table[.name] = sectionA table[.type] = type ---------[CALLED FUNC No.2]---------- table[.name] = sectionB table[.type] = type table[value] = hello table[.anonymous] = false table[.index] = 1 ---------[CALLED FUNC No.3]---------- table[.name] = sectionC table[.type] = type table[items][1] = 1 table[items][2] = 2 table[items][3] = 3 table[items][4] = 4 table[items][5] = 5 table[.anonymous] = false table[.index] = 2
- ----->Cursor:foreach関数仕様
- Cursor:get(config, section)
-
任意UCIコンフィグレーションファイルの指定オプション値を取得する関数です。
次は、sample.sectionB.valueの値を取得して変数valに格納するサンプルコードです。
-- get_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() local val = uci:get("sample", "sectionB", "value") print("sample.sectionB.value = " .. val) -
実行してみると、次のようにsample.sectionB.valueの現在値が取得できます。
root@OpenWrt:~# lua get_test.lua sample.sectionB.value = 100
- ----->Cursor:get関数仕様
- Cursor:get_all(config, section)
- 任意UCIコンフィグレーションファイルの指定セクションが持つ全オプション値を取得します。 次は、sampleコンフィグが持つオプション値を全て取得してコンソールに表示するサンプルコードです。
-
-- get_all_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() local sample = uci:get_all("sample") for key, val in pairs(sample) do for k, v in pairs(val) do if type(v) == "string" then print("sample[" .. key .. "][" .. k .. "] = " .. v) elseif type(v) == "boolean" then if v == true then print("sample[" .. key .. "][" .. k .. "] = true") else print("sample[" .. key .. "][" .. k .. "] = false") end end end end -
実行してみると、sampleコンフィグのboolセクションの全オプション値をLuaテーブルとして取得、コンソール上に表示します。
root@OpenWrt:~# lua get_all_test.lua sample[option][.name] = sectionB sample[option][.type] = type sample[option][value] = hello sample[option][.anonymous] = false sample[bool][flag2] = off sample[bool][.anonymous] = false sample[bool][flag3] = true sample[bool][flag4] = false sample[bool][flag6] = 0 sample[bool][flag5] = 1 sample[bool][flag1] = on sample[bool][.name] = sectionA sample[bool][.type] = type sample[list][.name] = sectionC sample[list][.type] = type sample[list][.anonymous] = false
- ----->Cursor:get_all関数仕様
- Cursor:get_bool(config, section, option)
-
オプションやリストデータが持つ特定文字列をLuaスクリプトの論理値であるtrue/falseに変換します。
論理値として変換される対象文字列は下表の通りです。
真(true) 偽(false) 'on' 左記以外 'true' 'yes' '1' - 次は、上記表の文字列を論理値に変換し、その結果をコンソールに表示するサンプルコードです。
-
-- get_bool_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() local flg = {} flg.result1 = uci:get_bool("sample", "sectionA", "flag1") -- 'on' flg.result2 = uci:get_bool("sample", "sectionA", "flag2") -- 'off' flg.result3 = uci:get_bool("sample", "sectionA", "flag3") -- 'true' flg.result4 = uci:get_bool("sample", "sectionA", "flag4") -- 'false' flg.result5 = uci:get_bool("sample", "sectionA", "flag5") -- '1' flg.result6 = uci:get_bool("sample", "sectionA", "flag6") -- '0' for key, val in pairs(flg) do io.write("flg." .. key .. " = ") if val == true then io.write("true\n") else io.write("false\n") end end
-
実行してみると、論理値を示す文字列が真(true)もしくは偽(false)に変換されます。
今回は、コンソール表示をするために"true"と"false"を出力するようにしています。
root@OpenWrt:~# lua get_bool_test.lua flg.result6 = false flg.result4 = false flg.result1 = true flg.result5 = true flg.result3 = true flg.result2 = false
- ----->Cursor:get_bool関数仕様
- Cursor:get_confdir()
- UCIコンフィグレーションファイルの格納ディレクトリ(フラッシュ領域)を文字列として取得します。2023年3月現在の実装では 戻り値が"/etc/config"としてハードコーティングされているため、常に"/etc/config"を返す関数になっています。
- 次はget_confdir関数を使用したサンプルコードです。
-
-- get_confdir_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() local flash_dir = uci:get_confdir() print("flash dir: " .. flash_dir) - 実行結果は以下の通りです。今後、フラッシュ領域のディレクトリ変更に対応した実装に変更される かもしれませんが、現在は自明の"/etc/config"が出力されます。
- ----->Cursor:get_confdir関数仕様
root@OpenWrt:~# lua get_confdir_test.lua flash dir: /etc/config
- Cursor:get_first (config, type, option, default)
- この関数は任意のタイプtypeをも持つ、匿名セクションの中で一番先頭の ものが持つオプションoptionの値を取得します。もし、対象オプションが存在しない場合は defaultの値を返します。
- 次はunnameタイプを持つ先頭の匿名セクション@unname[0]からvalueオプションの値を取得するサンプルコードです。
-
-- get_first_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() local value = uci:get_first("sample", "unname", "value", "not found") print(value) -
実行結果は以下の通りです。sample.@unname[0].valueが取得できることが分かります。
root@OpenWrt:~# lua get_first_test.lua 100
なお、この関数の存在から分かるように、OpenWrt専用アプリケーションは数ある 匿名セクションの中から一番先頭のセクション情報をプライオリティ設定として認識します。 - 全てのOpenWrt専用アプリケーションがこのような設定の優先度付けをしているわけではありませんが、 このことを覚えておくとアプリケーション開発に役立つかもしれません。
- ----->Cursor:get_first関数仕様
- Cursor:get_list(config, section, option)
- 任意UCIコンフィグレーションファイル(config)の指定セクション(section)のリスト(option)をLuaテーブルとして取得します。 次は、sampleコンフィグのlistセクション内にあるitemsリストを取得するサンプルコードです。
-
-- get_list_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() local table = uci:get_list("sample", "sectionC", "items") for idx, val in ipairs(table) do print("table[" .. idx .. "] = " .. table[idx]) end -
実行すると、次のようにLuaテーブルにリストの各データが格納されます。
root@OpenWrt:~# lua get_list_test.lua table[1] = 1 table[2] = 2 table[3] = 3 table[4] = 4 table[5] = 5
- ----->Cursor:get_list関数仕様
- Cursor:get_savedir()
- UCIコンフィグレーションファイルのステージング領域を文字列として取得します。2023年3月現在の実装では 戻り値が"/tmp/.uci"としてハードコーティングされているため、常に"/tmp/.uci"を返す関数になっています。
- 次はget_savedir関数を使用したサンプルコードです。
-
-- get_savedir_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() local staging_dir = uci:get_savedir() print("staging dir = " .. staging_dir) - 実行結果は以下の通りです。今後、ステージング領域のディレクトリ変更に対応した実装に変更される かもしれませんが、現在は自明の"/tmp/.uci"が出力されます。
- ----->Cursor:get_savedir関数仕様
root@OpenWrt:~# lua get_savedir_test.lua staging dir: /tmp/.uci
- Cursor:get_session_id() ※作成中です。
-
-- get_session_id_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() - ----->Cursor:get_session_id関数仕様
- Cursor:load(config)
- 対象のUCIコンフィグ<config>を手動ロードする関数です。 ただし、現在(2024/10/14時点)の実装を見てみると以下のように実行されたら無条件でtrueを返すようになっています。
-
-- /usr/lib/lua/luci/model/uci.luaのload関数定義の抜粋部 function load(self, config) return true end - 一応、調査したときに作成したサンプルコードを掲載します。
-
-- load_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() io.write("Input config name :") io.flush() local config = io.read() local result = uci:load(config) if result then print("loaded! (true)") else print("not found! (false)") end - ----->Cursor:load関数仕様
- Cursor:revert(config)
- ステージング領域(default:/tmp/.uci)に保存された任意のUCIコンフィグレーションファイルの変更差分を消去します。 次は、set関数によってステージング領域に保存したsampleコンフィグのvalueオプション値を消去するサンプルコードです。
-
-- revert_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() uci:set("sample", "sectionB", "value", "hello") uci:revert("sample") -
実行してみると、ステージング領域に保存されたvalueオプションの値である"hello"が消去されていることが確認できます。
(そのため、これは何の役にも立っていないスクリプトです。)
root@OpenWrt:~# lua revert_test.lua root@OpenWrt:~# uci changes sample root@Openwrt:~# #変更内容は消去されたので、何も表示されません - ----->Cursor:revert関数仕様
- Cursor:rollback() ※作成中です。
-
-- rollback_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() - ----->Cursor:rollback関数仕様
- Cursor:rollback_pending() ※作成中です。
-
-- rollback_pending_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() - ----->Cursor:rollback_pending関数仕様
- Cursor:save(config) ※作成中です。
-
-- save_test.lua function save(self, config) return true end - ----->Cursor:save関数仕様
- Cursor:section(config, type, name, values)
- 指定UCIコンフィグレーションファイル(config)に新しいタイプ(type)とセクション(name)、オプション(option)を追加し、その内容をステージング領域(default: /tmp/.uci)に保存します。 次は、sampleコンフィグに"new"タイプの"sectionD"セクションを追加し、配下にdata1とdata2オプションを追加するサンプルコードです。
-
-- section_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() local option = { data1 = "created!", data2 = "created!", } uci:section("sample", "new", "sectionD", option) -
実行すると、確かにsampleコンフィグの新たなデータとしてnewセクションのdata1とdata2オプションがステージングされることが確認できます。
root@OpenWrt:~# lua section_test.lua root@OpenWrt:~# uci changes sample.sectionD='new' sample.sectionD.data1='created!' sample.sectionD.data2='created!'
- ----->Cursor:section関数仕様
- Cursor:set(config, section, option, value)
-
LuCI連携なし
任意UCIコンフィグレーションファイルの指定セクションに対するオプションの新規追加または値変更をします。 変更内容はステージング領域(default: /tmp/.uci)の対応するUCIコンフィグレーションファイルに保存されます。 次はsample.sectionB.valueの値を初期値の"100"から"hello"に変更するサンプルコードです。 -
-- set_test1.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() uci:set("sample", "sectionB", "value", "hello") -
実行してみると、ステージング領域に変更内容が保存されることが確認できます。
通常、続いてcommit関数を実行することでフラッシュ領域に変更内容がコピー(マージ)されます。
root@OpenWrt:~# lua set_test.lua root@OpenWrt:~# uci changes sample.sectionB.value='hello'
-
LuCI連携あり
set_session_idでセッション番号をuciオブジェクトに割り当てた場合、uci:setによって変更または追加されたパラメーターの ステージング領域は/tmp/.uciではなく、セッション番号に紐づけられたメモリ領域になります。 - 次はセッション番号指定によって、それに対応するメモリ領域を確保した上でsample.sectionB.valueの値を初期値の"100"から"hello"に変更するサンプルコードです。
-
-- set_test2.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() local result = uci:set_session_id("0479472194661836394729210") if result then local id = uci:get_session_id() print("success : id =" .. id) else print("failed") return end uci:set("sample", "sectionB", "value", "hello") - 動作確認はubus monitorコマンドを実行した後に本サンプルコードを実行します。
-
root@OpenWrt:~# ubus monitor & root@OpenWrt:~# lua set_test2.lua
- 実行してみると以下のようにセッション番号と対応するメモリ領域に変更内容が記録されたことがわかります。 メモリ領域を管理しているのは/sbin/rpcdです。
- ----->Cursor:set関数仕様
-- ubus monitorコマンドの出力結果の抜粋です。実際はもっと大量のメッセージが出力されます。
-> 6f38264a #00000000 status: {"status":0}
<- 6f38264a #4b12e34c invoke: {"objid":1259529036,"method":"set","data":{"ubus_rpc_session":"0479472194661836394729210","config":"sample","values":{"value":"hello"},"section":"sectionB"}}
-> 72395126 #6f38264a invoke: {"objid":1259529036,"method":"set","data":{"ubus_rpc_session":"0479472194661836394729210","config":"sample","values":{"value":"hello"},"section":"sectionB"},"user":"root","group":"root"}
- Cursor:set_confdir(directory) ※作成中です。
-
-- set_confdir_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() - ----->Cursor:set_confdir関数仕様
- Cursor:set_list(config, section, option, value)
- 任意UCIコンフィグレーションファイル(config)の指定セクション(section)配下にリストデータ(option)を作成し、その変更内容(value)を ステージング領域(default: /tmp/uci)に保存します。第三引数にLuaテーブルを指定することで一度 に複数のデータを追加することが可能です。指定したセクションが既に存在する場合、既存リストデータは消去され、新しいデータで上書きされます。
- 次は、sampleコンフィグの"sectionC"セクションに新たなリストデータgreetingsを作成するサンプルコードです。 追加するデータは3つ('good morning'、'hello'、'good bye')です。
-
-- set_list_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() local words = { "good morning", "hello", "good bye", } uci:set_list("sample", "sectionC", "greetings", words) -
実行してみると、"sectionC"セクションにgreetingsが3つのデータを持った状態で作成され、その変更内容が
ステージング領域に保存されることが確認できます。
root@OpenWrt:~# lua set_list_test.lua root@OpenWrt:~# uci changes sample.sectionC.greetings+='good morning' sample.sectionC.greetings+='hello' sample.sectionC.greetings+='good bye'
- ----->Cursor:set_list関数仕様
- Cursor:set_session_id(id)
- LuCIのユーザーアクセスに応じたセッションを作成する関数です。任意のセッションID<id>を引数に 指定して実行します。
-
-- set_session_id_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() local result = uci:set_session_id("0479472194661836394729210") if result then local id = uci:get_session_id() print("success : id =" .. id) else print("failed") end - この関数によってセッションIDに紐づいたUCIのステージング領域がRAM内に作成されます。 これにより、load・apply・rollback・save・set_savedirなどが利用可能になります。
- ----->Cursor:set_session_id関数仕様
- Cursor:substate() ※作成中です。
-
-- substate_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() - ----->Cursor:substate関数仕様
- Cursor:tset(config, section, values)
- 指定UCIコンフィグレーションファイル(config)の既存セクション(section)に対して、オプション(values)を追加し、その内容をステージング領域(default: /tmp/.uci)に保存します。 追加するオプションはテーブルデータとして定義し、第三引数に指定することで対象セクションに追加することが可能です。 これにより、一度に複数のオプションを追加することが出来ます。
- 次は、sampleコンフィグの既存セクション「sectionB」に3つの新規オプション(greeting1~3)を追加するサンプルコードです。
-
-- tset_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() local new_options = { greeting1 = "good morning", greeting2 = "hello", greeting3 = "good bye", } uci:tset("sample", "sectionB", new_options) -
実行すると、既存セクションの「sectionB」に新たなオプション(greeting1~3)が追加され、その内容がステージング領域に保存されることが
確認出来ます。
root@OpenWrt:~# lua tset_test.lua root@OpenWrt:~# uci changes sample.sectionB.greeting3='good bye' sample.sectionB.greeting1='good morning' sample.sectionB.greeting2='hello'
- ----->Cursor:tset関数仕様
- Cursor:unload(config) ※作成中です。
-
local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() - ----->Cursor:unload関数仕様
- Cursor:reorder(config, section, index)
-
LuCI連携なし
reorder関数は任意のUCIコンフィグレーションファイルのセクションの配置を変更します。 配置変更したセクションはステージング領域(default: /tmp/.uci)に保存されます。 静的データとして確定したい場合は、commit関数によってフラッシュ領域(default: /etc/config)にコピー(マージ)する必要があります。 - 次はsample.@unname[1]をsample.@unname[0]に配置変更するサンプルコードです。
-
-- reorder_test.lua local uci = require("luci.model.uci").cursor() local section = "" local index = 0 uci:foreach("sample", "unname", function(tbl) index = index + 1 -- unameタイプで2番目の匿名セクション@unname[2]のUIDを取得 if index == 2 then section = tbl[".name"] end end) if #section == 0 then print("Not Found.") end uci:reorder("sample", section, 1) -- 一番先頭に配置変更する
- 上記のスクリプトを以下のように実行した後、uci showでセクションの出現順を見てみると、 sample.@unname[1]の内容がsample.@unname[0]に移動しており、sample.@unname[0].value=200に なっていることが確認できます。
-
root@OpenWrt:~# lua reorder_test.lua root@OpenWrt:~# uci show sample
関連記事
- OpenWrt UCIコマンドの使い方
- OpenWrt サンプルプログラム掲載! UCIコマンド用C言語ライブラリ - libuci
- OpenWrt シェルスクリプト専用UCI関数の使い方
- OpenWrt Luaスクリプト専用UCI関数の使い方
- OpenWrt UBUSコマンドの使い方
- OpenWrt サンプルプログラム掲載! UBUS用C言語ライブラリ-libubus(object・method登録実装)
- OpenWrt サンプルプログラム掲載! UBUS用C言語ライブラリ-libubus(listenコマンド実装)
- OpenWrt サンプルプログラム掲載! UBUS用C言語ライブラリ-libubus(sendコマンド実装)
参考文献
- Object Instance luci.model.uci: https://openwrt.github.io/luci/api/modules/luci.model.uci.html